Santos Mañes
Group Leader
Research summary
Inflammation is essential for effective defence of the organism against harmful stimuli such as pathogens, irritants or tissue damage. Discovery of the detailed processes of inflammation has revealed a close relationship between the inflammatory reaction and the immune response. Indeed, a hallmark of inflammation is the directed migration (chemotaxis) of inflammatory cells (mostly leukocytes) through blood vessel walls to the site of injury. Nonetheless, a deregulated response to tissue damage might lead to autoimmunity and chronic inflammatory diseases, and can also promote cancer.
Publications
Mira E, Carmona-Rodríguez L, Pérez-Villamil B, Casas J, Fernández-Aceñero MJ, Martínez-Rey D, Martín-González P, Heras-Murillo I, Paz-Cabezas M, Tardáguila M, Oury TD, Martín-Puig S, Lacalle R, Fabriás G, Díaz-Rubio E, Mañes S. SOD3 improves the tumor response to chemotherapy by stabilizing endothelial HIF-2α. Nature Communications 2018; 9:389
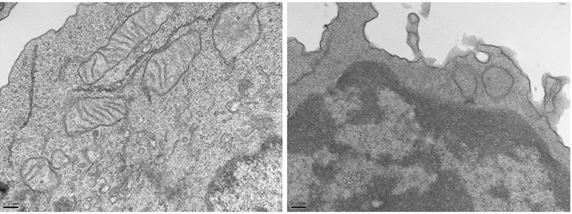
Ogando J, Sáez ME, Santos J, Nuevo-Tapioles C, Gut M, Esteve-Codina A, Heath S, González-Pérez A, Cuezva JM, Lacalle RA, Mañes S. PD-1 signaling affect cristae morphology and leads to mitochondrial dysfunction in human CD8+ T lymphocytes. J Immunother Cancer 2019; 7:151
Martín-Leal A, Blanco R, Casas J, Sáez ME, Rodríguez-Bovolenta E, de Rojas I, Drechsler C, Real LM, Fabrias G, Ruíz A, Castro M, Schamel WW, Alarcón B, van Santen HM, Mañes S. CCR5 deficiency impairs CD4+ T-cell memory responses and antigenic sensitivity through increased ceramide synthesis. EMBO J 2020; 39:e104749
Carmona-Rodríguez L, Martínez-Rey D, Fernández-Aceñero MJ, González-Martín A, Paz-Cabezas M, Rodríguez-Rodríguez N, Pérez-Villamil B, Sáez ME, Díaz-Rubio E, Mira E, Mañes S. SOD3 induces a HIF-2α-dependent program in endothelial cells that provides a selective signal for tumor infiltration by T cells. J Immunother Cancer 2020; 8: e000432
Quintela-Fandino M, Holgado E, Manso L, Morales S, Bermejo B, Colomer R, Apala JV, Blanco R, Muñoz M, Caleiras E, Iranzo V, Martinez M, Dominguez O, Hornedo J, Gonzalez-Cortijo L, Cortes J, Gasol Cudos A, Malon D, Lopez-Alonso A, Moreno-Ortíz MC, Mouron S, Mañes S. Immuno-priming durvalumab with bevacizumab in HER2-negative advanced breast cancer: a pilot clinical trial. Breast Cancer Res 2020; 22:124
Immune evasion is a fundamental hallmark of cancer. The immune system recognizes tumour cell-derived neoantigens and generates tumour-specific T cell responses, distinguishing neoplastic from healthy cells. But cancers escape this control. Despite the initial high hopes of immunotherapy, complete durable responses are still rare. We aim to identify, understand and manipulate tumour-induced resistance mechanisms and to develop new immunotherapies against cancer. These are our research topics:
- Normalization of tumour-associated vasculature to improve immunotherapy
Angiogenesis is a common feature of cancer. Tumour vessels are, however, dysfunctional, leading to hypoxia and tumour aggressiveness. We are working on basic aspects of a new normalizer of the vasculature (SOD3), and collaborate in clinical trials to demonstrate the synergistic activity of anti-angiogenic and immunotherapy in breast cancer treatment..
- Signalling pathways involved in T cell dysfunction
Tumour-specific T cells are usually dysfunctional in the tumour microenvironment (TME). Using RNA-seq and bioinformatics, we identified a genetic program associated to T cell exhaustion. In collaboration with Industry, we are deciphering the mechanisms of new intermediates causing T cell dysfunction and their potential clinical application.
- Metabolic cues affecting T cell function in the TME
Metabolic reprogramming is another new hallmark of cancer. Neoplastic cells develop a number of metabolic adaptations to survive and proliferate without restrictions, but also induce metabolic stress affecting the activity of endothelial and T cells in the TME. We aim to manipulate the metabolism of tumour, endothelial and T cells to turn an immunosuppressive TME into an immunodominant one.
- CD4 T cell differentiation in the TME.
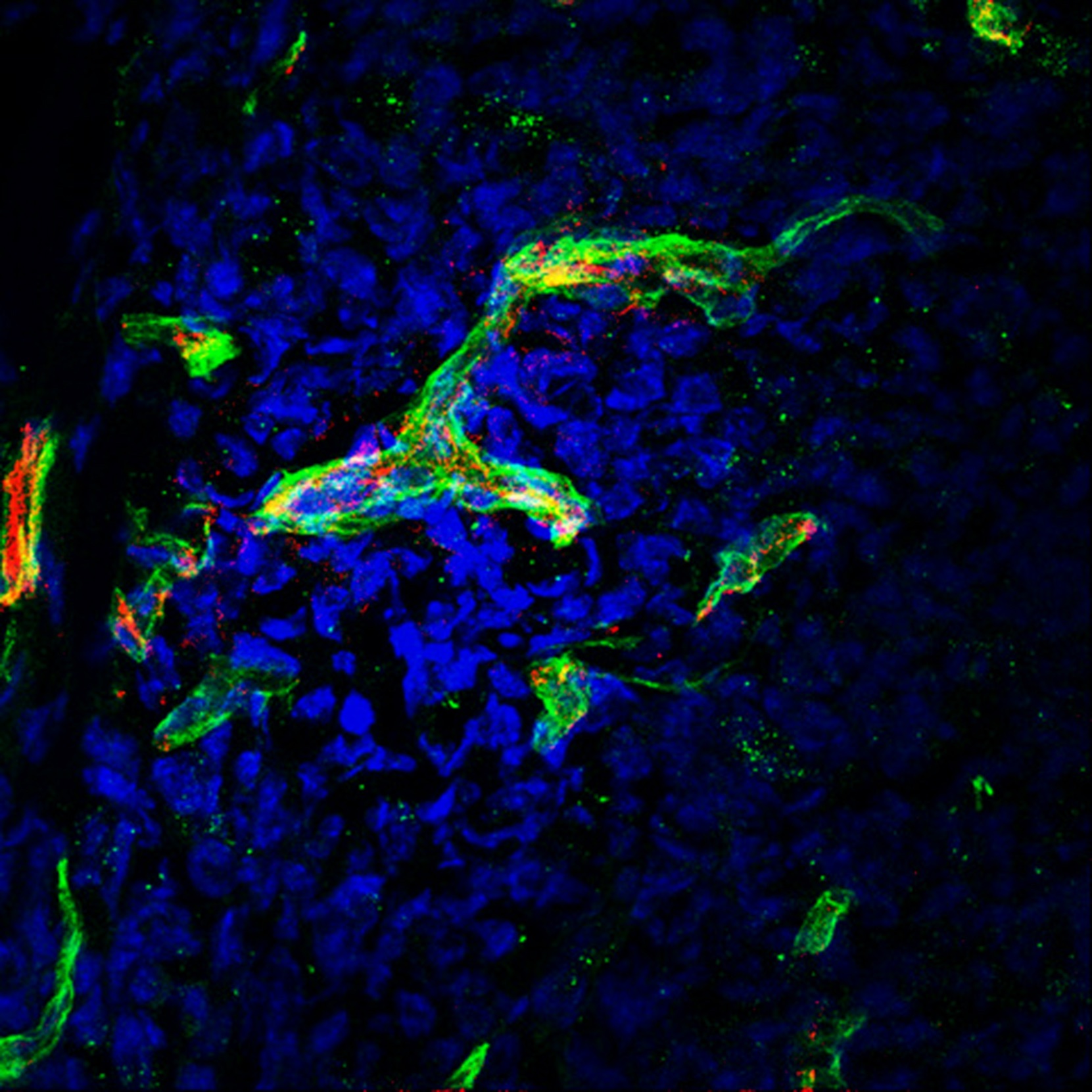
The number and nature of the immune populations that infiltrate tumors determine the immune-mediated control of cancer and the response to immunotherapy. The cells may come from the bloodstream or lymph, or can be differentiated in the TME. We are investigating the function of the extracellular matrix in the generation of immunosuppressive immune cell phenotypes and its relevance in tumour progression.