Fernando Rojo
Group Leader
Research summary
Our aim is to characterize the global regulation networks responsible for catabolite repression, identifying their components, the signals to which they respond, and the molecular mechanisms by which they regulate gene expression. The regulatory proteins involved in these networks are different in distinct microorganisms.
Publications
Gómez-García G, Ruiz-Enamorado A, Yuste L, Rojo F*, Moreno R*. Expression of the ISPpu9 transposase from Pseudomonas putida KT2440 is regulated by two small RNAs and a long and structured 5´-untranslated region. Nucleic Acids Research 2021; 49: 9211-9228
Molina L, La Rosa R, Nogales J, Rojo F. Influence of the Crc global regulator on substrate uptake rates and the distribution of metabolic fluxes in Pseudomonas putida KT2440 growing in a complete medium. Environ Microbiol 2019; 21: 4446-4459.
Molina L, La Rosa R, Nogales J, Rojo F. Pseudomonas putida KT2440 metabolism undergoes sequential modifications during exponential growth in a complete medium as compounds are gradually consumed. Environ Microbiol 2019; 21: 2375-2390.
Val-Calvo J, Luque-Ortega JR, Crespo I, Miguel-Arribas A, Abia D, Sánchez-Hevia D, Serrano E, Gago-Córdoba C, Ares S, Alfonso C, Rojo F, Wu LJ, Boer R, Meijer WJJ. Novel regulatory mechanism of establishment genes of conjugative plasmids. Nucleic Acids Res 2018; 46: 11910-11926.
Sánchez-Hevia D, Yuste L, Moreno R, Rojo F. Influence of the Hfq and Crc global regulators on the control of iron homeostasis in Pseudomonas putida. Environ Microbiol 2018; 20: 3484-3503.
To be competitive in the environments they colonise, bacteria must optimise metabolism to attain maximum gain from available nutrients. Not all potential carbon sources are equally effective in this respect. For this reason, when confronted with a mixture of potentially assimilable compounds at sufficient concentrations, many bacteria preferentially use one of them, leaving others aside until the preferred one is consumed. This implies a complex regulatory process termed catabolite repression. Unravelling the molecular mechanisms involved helps understanding how bacteria coordinate their metabolism and gene expression programs and optimise growth. It also aids in the design and optimisation of biotechnological processes and to understand how bacteria degrade compounds in Nature.
The regulators and molecular mechanisms responsible for catabolite repression differ among microorganisms. Our work is focused on Pseudomonas putida, a bacterium with a versatile and robust metabolism much used in biotechnology. Catabolite repression relies on a complex regulatory network that includes the Crc and Hfq proteins, which inhibit translation of mRNAs containing a specific A-rich sequence motif within their translation initiation region. Two small RNAs, CrcZ and CrcY, the levels of which vary greatly depending on growth conditions, antagonise the inhibitory effect of Hfq and Crc. Our aim is to characterise the influence of Crc, Hfq, CrcZ and CrcY in the physiology of P. putida, the signals to which they respond, and the molecular mechanisms by which they regulate gene expression.
In addition, we have analysed the role of Hfq in other processes such as iron homeostasis and the regulation of ISPpu9, an insertion sequence of P. putida KT2440 in which we have observed that translation of the transposase gene mRNA is inhibited by a highly structured 5’ untranslated region, effect that is counteracted by an antisense small RNA and further modulated by a second small RNAs.
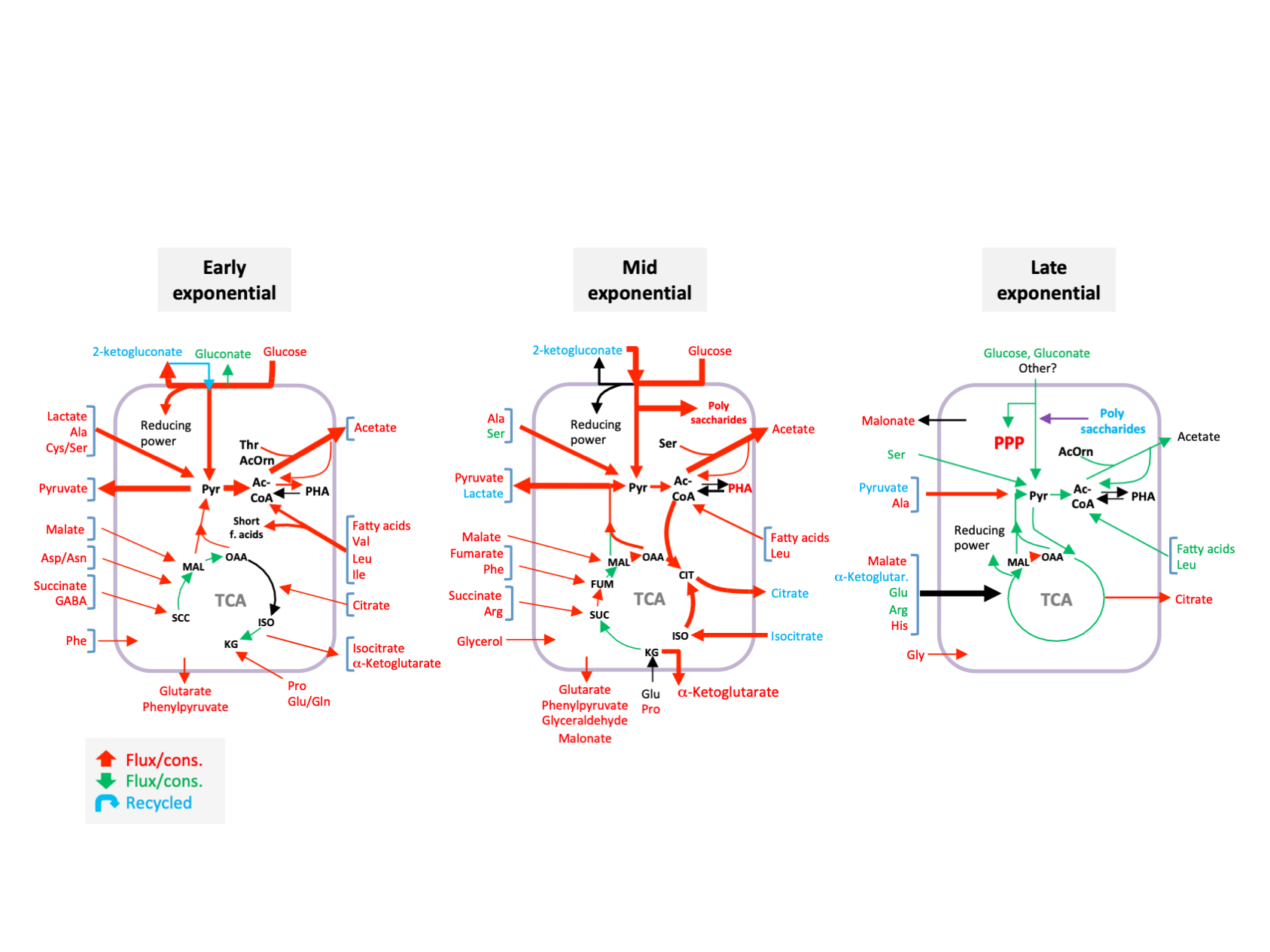
Figure legend. Effect of inactivating the crc gene on the configuration of the metabolite fluxes related to central carbon metabolism during early, mid and late exponential growth. The fluxes that increased (in red), decreased (in green), or remained unchanged (in black) in the Crc-null strain as compared to the wild type, are highlighted. Compounds that were released to the medium and later recycled are indicated in blue.








