Mario Mellado
Group Leader
Research summary
Through their interactions with G protein-coupled receptors, the chemokines have a key role in a broad array of biological responses that include cell polarisation and movement, immune and inflammatory responses, haematopoiesis, tumour rejection and prevention of HIV-1 infection.
Publications
Gardeta SR, García-Cuesta EM, D'Agostino G, Soler Palacios B, Quijada-Freire A, et al. Sphingomyelin depletion inhibits CXCR4 dynamics and CXCL12-mediated directed cell migration in human T cells. Front Immunol 2022, 13:925559.
García-Cuesta EM, Rodríguez-Frade JM, Gardeta SR, D'Agostino G, Martínez P, et al. Altered CXCR4 dynamics at the cell membrane impairs directed cell migration in WHIM syndrome patients. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2022 119(21):e2119483119.
Bovolenta ER, García-Cuesta EM, Horndler L, Ponomarenko J, Schamel WW et al. A set point in the selection of the αβTCR T cell repertoire imposed by pre-TCR signaling strength. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2022 119(22):e2201907119.
Cáceres-Martell Y, Fernández-Soto D, Campos-Silva C, García-Cuesta EM, Casasnovas JM, et al. Single-reaction multi-antigen serological test for comprehensive evaluation of SARS-CoV-2 patients by flow cytometry. Eur J Immunol 2021, 51(11):2633-2640.
Soler Palacios B, Nieto C, Fajardo P, González de la Aleja A, Andrés N, et al. Growth hormone reprograms macrophages towards an anti-inflammatory and reparative profile in a MAFB-dependent manner. J Immunol 2020; 205:776-788.
Lamana A, Villares R, Seoane VI, Andrés N, Lucas P, et al. Identification of a human SOCS1 polymorphism that predicts rheumatoid arthritis severity. Front Immunol 2020; 11: 1336.
Cell migration involves myriad signaling proteins and receptors that act coordinately to activate intracellular pathways and promote polarised cell states and directional migration. To migrate directionally in response to external stimuli, the internal machinery of cells needs to be spatially organised, which involves the integration of biochemical and mechanical factors to generate force in a specific direction to move the cell forward.
Chemokine receptors are membrane-expressed seven-transmembrane receptors linked to G proteins. Through interaction with the corresponding ligands, they induce a wide variety of cellular responses including cell polarisation, movement, immune and inflammatory responses, as well as prevention of HIV-1 infection. For achieving their function, chemokine receptors undergo ligand-dependent conformational changes that are influenced by the local cellular microenvironment.
Using quantitative single-molecule spatio-dynamic imaging, our group studies how the formation of large receptor nano-clusters in response to the ligand is critical for the maintenance of correct actin dynamics in migrating cells that allows directed cell migration. We have determined that altered cluster formation, using natural mutant chemokine receptors or altering the lipid composition of the cell membrane, results in the inability of these cells to correctly sense chemokine gradients. This inability to form clusters is responsible of the complex phenotype manifested by individuals carrying this mutated receptor and suggest that receptor clustering can be exploited as therapeutic target in inflammatory diseases and cancer.
In addition, our group is also involved in studying the effect of Growth hormone (GH) pretreatment of immune cells and its functional relevance. For instance, we observe that GH treatment prevents inflammatory joint destruction in a CIA model or that GH improved remission of inflammation and mucosal repair during recovery in the acute dextran sodium sulfate-induced colitis. The effects occur in several immune cells, i.e. GH reprograms inflammatory macrophages to an anti-inflammatory phenotype and improves resolution during pathologic inflammatory responses.
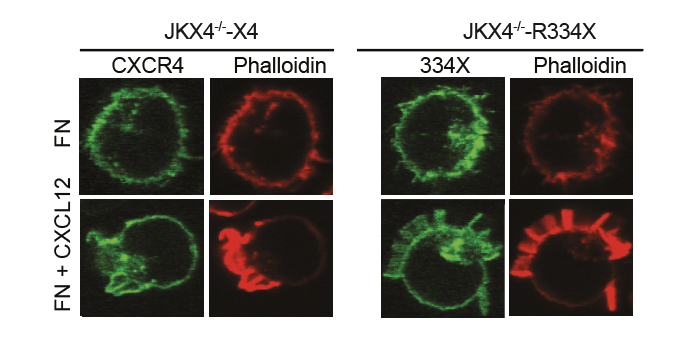
Figure 1. CXCL12 induces multiple lamellipodia through interaction with mutant CXCR4R334X. F-actin (phalloidin-TRITC, red) and CXCR4 (AcGFP, green) visualized by confocal microscopy in JKX4-/--X4 and JKX4-/--R334X cells adhered to fibronectin and treated or not with CXCL12.
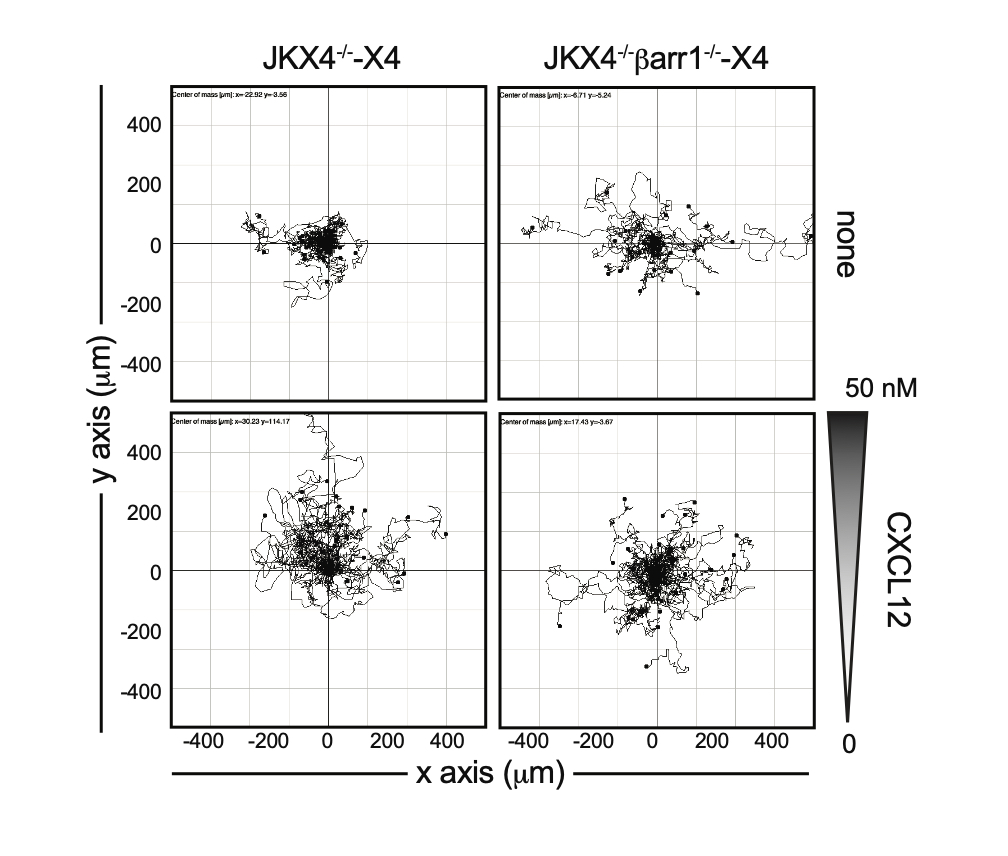
Figure 2. b-arrestin regulates directional cell migration in response to CXCL12. Spider plots showing the trajectories of tracked JKX4-/--X4 and JKX4-/-barr-/--X4 cells migrating on fibronectin-coated m-slide chemotaxis chambers along a CXCL12 gradient.








