Inés Antón
Group Leader
Research summary
Essential processes such as neuronal morphogenesis, cell motility and tissue invasion rely on the spatial and temporal regulation of actin dynamics and therefore, their deregulation is at the root of severe pathologies. Actin reorganization is controlled by nucleation-promoting factors like neural Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome protein (N-WASP) and cortactin, and associated proteins that regulate their activity such as WIP (WASP-interacting protein), a ubiquitously distributed protein that stabilizes actin filaments. Our goal is to define the role of WIP- and WASP-family proteins in actin dynamics within a variety of cellular processes in fibroblasts, dendritic cells (DC), neurons and astrocytes.
Publications
Escoll M et al. WIP Modulates Oxidative Stress through NRF2/KEAP1 in Glioblastoma Cells. Antioxidants (Basel). 2020; 9:773-785.
Antón IM, Gómez-Oro C, Rivas S, Wandosell F. Crosstalk between WIP and Rho family GTPases. Small GTPases. 2020; 11:160-166.
Menotti M et al. Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome protein (WASP) is a tumor suppressor in T cell lymphoma. Nat Med. 2019; 25:130-140.
Escoll M, Gargini RA, Cuadrado A, IM Anton, Wandosell F. Mutant p53 oncogenic functions in cancer stem cells are regulated by WIP through YAP/TAZ. Oncogene 2017; 36:3515-3527
Gargini RA, Escoll M, García E, García-Escudero R, Wandosell F, IM Anton. WIP drives tumor progression to promote YAP/TAZ-dependent autonomous cell growth. Cell Reports 2016; 17 (8):1962-1977
García E, Ragazzini, C, Yu X, Cuesta-García E, Zech T, Sarrio D, Machesky LM, IM Anton. WIP and WICH/WIRE co-ordinately control invadopodium formation and maturation in human breast cancer cell invasion. Scientific Reports 2016; 6:23590
Actin cytoskeleton is an essential contributor to cell motility and invasiveness and therefore understanding the molecules and mechanisms which regulate its temporal and spatial re-organization is vital to fight tumour invasion and metastasis, the cause of 90% of cancer-related deaths.
We study the role of actin-related proteins, mainly (N-)WASP (neural Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome protein), WIP (WASP interacting protein), TAZ (Transcriptional coactivator with PDZ-binding motif) and YAP (Yes-associated kinase), in tumour generation, progression and dissemination, mostly focusing in central nervous system tumours such as deadly gliomas. Through the analysis of glioblastoma samples using biochemical and molecular approaches, in combination with lentivirus-mediated modification of protein expression and advanced imaging analysis, mouse models and proteomics, we have described that WIP acts as a proto-oncogene; WIP overexpression is sufficient to transform primary human astrocytes following pathways which include Pak, formins (mDia) and the GTPase Rac. WIP levels directly correlate with cell proliferation, anchorage-independent growth, stemness and invasive capability and they also control the cellular amount of the co-transcriptional regulators and mechanosensors TAZ and YAP by protecting them from calpain or proteasome-mediated degradation. In contrast, in haematological malignancies (T cell lymphoma), WASP and WIP turn into tumour suppressors as ALK+ lymphomas developed by transgenic NPM-ALK mice are accelerated in WASP- and WIP-deficient mice.
At present we are following a systematic proteomics approach by mass spectrometry to search for common and unique partners in the WIP interactomes identified from glioblastoma versus hematological samples. We hope to identify novel therapeutical targets to find additional and effective cancer treatments. Our ultimate goal is to understand the molecular basis of the mechanism that regulates actin dynamics, a process that underlies numerous essential cellular functions whose deregulation leads to serious human diseases. We thus hope to provide new diagnostic, prognostic and/or therapeutic tools for neurological disorders, tumour initiation and metastasis.
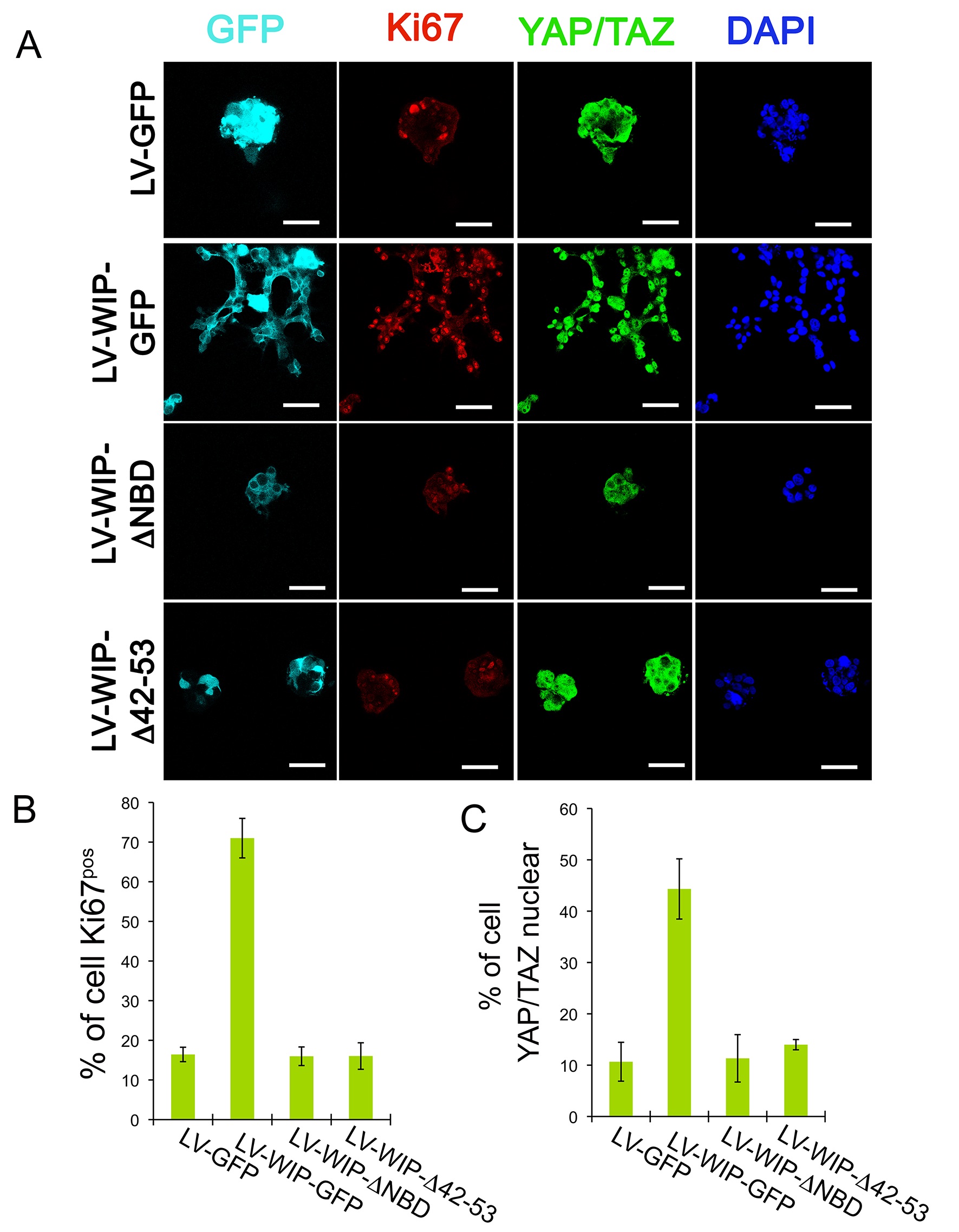
WIP binding to Nck and actin coordinates survival and proliferation to drive cell invasiveness in a YAP/TAZ-dependent manner. MDA-MB-468 cells were transduced with lentivirus encoding GFP, WIP-GFP, WIP-ΔNBD (WIP mutant lacking the Nck binding domain) or WIP-Δ42/53. (WIP mutant lacking the actin binding domain). (A) Confocal images of staining for GFP (cyan), proliferation marker Ki67 (red), YAP/TAZ (green) and nuclei (DAPI, blue) of invasive/non-invasive structures in 3D-Matrigel; bars, 25 μm. (B) Percentage of cells that showed positive staining for Ki67 or (C) nuclear localization of YAP/TAZ.