Jorge Vicente Conde
Ramón y Cajal researcher
Research summary
We are studying how plants translate information from pathogen sensing to an effective immune response by controlling the abundance of key defence-related proteins. The major goal is to be able to define the fate of essential defence proteins in which their conditional stability is controlled by the biochemical system called the N-degron pathways. By determining new key regulatory proteins whose quantity is regulated to enhance plant defence we will improve biotechnological and classical breeding approaches to secure yields against pathogens.
Publications
Barreto P, Dambire C, Sharma G, Vicente J, Laitz A, et al. Mitochondrial retrograde signalling through UNCOUPLING PROTEIN 1-mediated inhibition of the plant oxygen-sensing pathway. Current Biology 2022, 32 (6):1403-11.
Till CJ, Vicente J, Zhang H, Oszvald M, Deery MJ, et al. The Arabidopsis thaliana N-recognin E3 ligase PROTEOLYSIS1 influences the immune response. Plant Direct 2019, 3: 1-15.
Vicente J, Mendiondo GM, Pauwels J, Pastor V, Izquierdo Y, et al. Distinct branches of the N-end rule pathway modulate the plant immune response. New Phytologist, 2019, 221: 988–1000.
Vicente J, Mendiondo GM, Movahedi M, Peirats-Llobet M, Juan Y, et al. The Cys-Arg/N-end rule pathway is a general sensor of abiotic stress in flowering plants. Current Biology 2017, 27: 1-8.
Funding
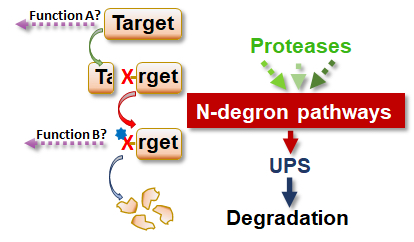
A prerequisite for global food security is controlling pathogenic infections that increasingly decimate crops yields. In this fight a fundamental goal is the identification of proteins that activate and enhance the plant immune response. However, little is known about how the stability of these proteins, that greatly affects their activity, is regulated. We are addressing the hypothesis that the N-degron pathways, a biochemical system of protein degradation, is an undiscovered mechanism that controls the abundance of key defence protease targets during plant defence against pathogens.
The N-degron pathways control protein degradation by recognition of an N-degron, a specific motif determined primarily by an amino-terminal (Nt-) destabilizing amino acid residue. This is produced by endo-peptidase action and recognized by a specific class of E3 ligases (N-recognins), targeting the proteins for degradation via the Ubiquitin Proteosome System (UPS). As endo-peptidase activity is required to expose Nt- residues on substrate proteins, therefore, combined protease cleavage and N-degron targeting activities can determine the fate of polypeptides. Plants have a large number of protease coding genes in plant genomes, though almost no substrates of these proteases have been identified. In collaboration with groups of the University of Nottingham (UK) and VIB (Belgium), we have used protease degradomes obtained from a combined state-of-the-art proteomic approach to identify dozens of protease targets as N-degron pathway substrates in vivo. Among them are key regulators of plant defence and development signalling.
Therefore, it should be possible to track the fate of a substantial subset of protease targets by analysing their N-degron pathways half-life dependency. Now, we aim to:
- i) Understand the molecular mechanism associated with substrate function in plant defence.
- ii) Analyse the role of these pathways in sensing molecules from pathogens (PAMPs).
- iii) Study of the coordinating role of the N-degron pathways between proteolytic systems.
- iv) Test the usefulness of substrates in crops, starting in tomato.
The study of the combined protease cleavage and N-degron pathways targeting activities can provide unique knowledge about how the abundance of key defence proteins is controlled during infections.


 Laboratory Members
Laboratory Members



