Rubén García Martín
Ramón y Cajal researcher
Research summary
The main goal of our lab is to shed light on the fundaments of the intercellular and interorgan crosstalk mediated by extracellular vesicles, lipoproteins and protein complexes in living organisms, their role in the regulation of physiological processes with a special focus on metabolism and how their dysregulation could drive the development of metabolic disorders, cardiovascular diseases, cancer and immune system pathologies.
Publications
Garcia-Martin R, Wang G, Brandao BB, Zanotto TM, Shah S, Patel SK, Schilling B, Kahn CR MicroRNA sequence codes for small extracellular vesicle release and cellular retention, Nature 2022, 601(7893):446-451.
Garcia-Martin R, Brandao BB, Thomou T, Altindis E, Kahn CR. Tissue differences in the exosomal/small extracellular vesicle proteome and their potential as indicators of altered tissue metabolism. Cell Reports, 2022, 38(3):110277.
Srinivasa S, Garcia-Martin R, Torriani MD, Fitch KV, Carlson A, Kahn CR, Grinspoon SK. Altered Pattern of Circulating miRNAs in HIV Lipodystrophy Perturb Key Adipose Differentiation and Inflammation Pathways. JCI Insight 2021, 6(18):e150399.
Mori M, Ludwig R, Garcia-Martin R, Brandao BB, Kahn CR. Extracellular miRNAs: From Biomarkers to Mediators of Homeostasis and Disease. Cell Metabolism, 2019. 30(4):656-673.
Thomou T, Mori MA, Dreyfuss JM, Konishi M, Sakaguchi M, Wolfrum C, Rao TN, Winnay JN, Garcia-Martin R, Grinspoon SK, Gorden P, Kahn CR. Adipose-derived circulating miRNAs regulate gene expression in other tissues. Nature. 2017 Feb 23;542(7642):450-455.
Funding
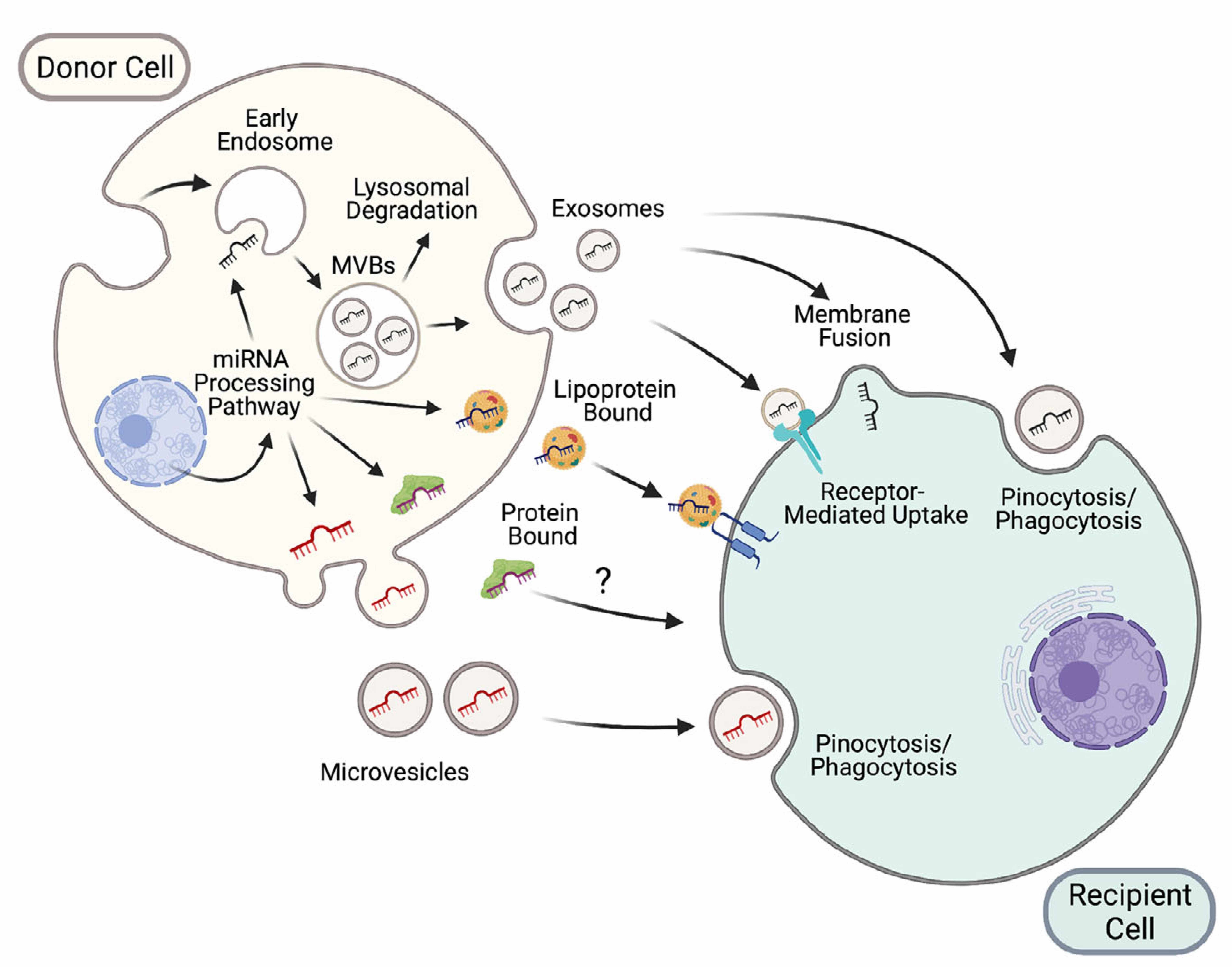
Figure 1: New modes of intercellular communication among nearby and distant cells (located in other organs), including extracellular vesicles (exosomes and microvesicles), lipoproteins and protein complexes. (Extracted from Brandao et al, J of Physiol 2022, 600.5 pp1155-1169).
We have recently shed light into the mechanism guiding the sorting of one of the major constituents of these carriers, microRNAs, in extracellular vesicles by cells in vitro (Garcia-Martin et al, Nature 2022). Short sequence codes determine the vesicular sorting (EXOmotifs) or cellular retention (CELLmotifs) of microRNAs (Fig. 2).
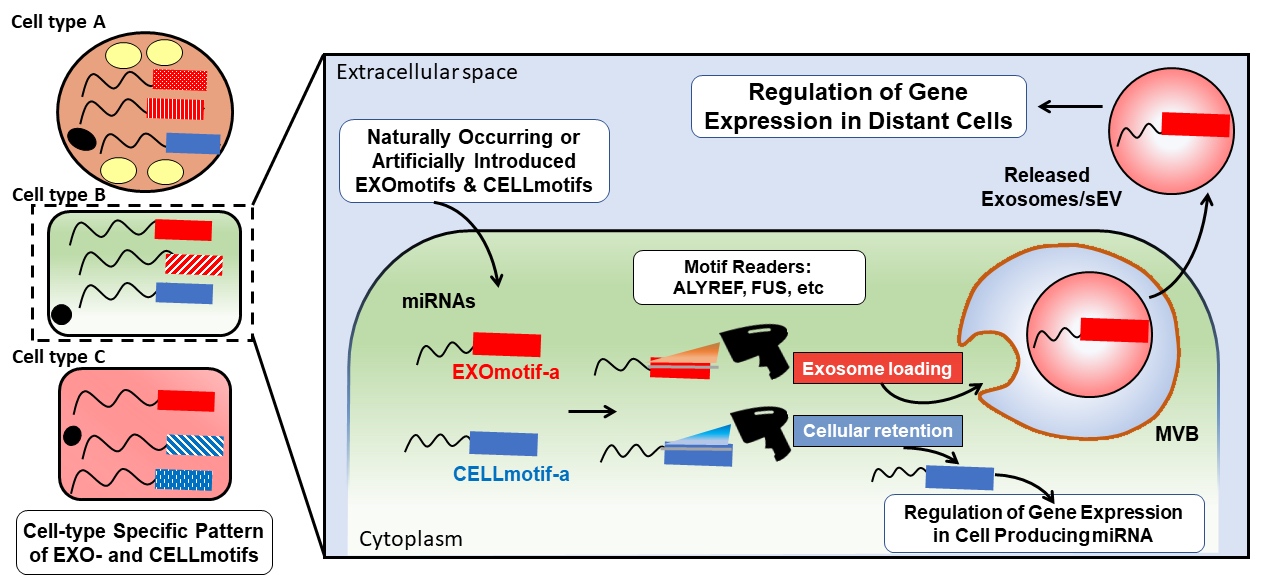
Figure 2: each cell type has a specific pattern of EXO- and CELL-motifs regulating exosomal loading and cellular retention of microRNAs, respectively. Some proteins such as ALYREF and FUS are able to read those codes and mediate vesicular loading (Extracted from Garcia-Martin et al, Nature 2022, 601:446-451).
Besides, we characterized the cargo signature of extracellular vesicles released by multiple metabolic cell types; information that can be used to predict tissue-of-origin of these vesicles in the circulation of a metabolic disease model (Garcia-Martin et al, Cell Reports, 2022). However, most key aspects of these communication systems remain largely unknown, especially in vivo, such as the cells of origin of these carriers in systemic circulation, the mechanisms guiding the selection of most types of cargo, the drivers of selective trafficking and the final function that those communication events mediate in recipient cells. Importantly, these novel modes of communication, besides allowing the coordinated crosstalk among most tissues of our bodies for regulating physiological processes, also play an important role in the development of a vast list of pathologies, such as metabolic diseases, cancer, autoimmune disorders, cardiovascular diseases. In this regard, we recently showed that the content of extracellular vesicles participates in the development of lipodystrophy in HIV patients (Srinivasa, Garcia-Martin et al, JCI Insight 2021). Thus, if a better understanding of the biology of these novel communication systems is achieved, it could result in innovative diagnostic and therapeutic applications for many diseases.


 Laboratory Members
Laboratory Members



