José M. Casasnovas
Group Leader
Research summary
Our group researches on receptor-ligand recognition using biochemical techniques and X-ray crystallography, studying receptors of the immune system, some of which have been subverted by viruses to enter into host cells.
Publications
Martínez-Fleta P, Alfranca A, González-Álvaro I, Casasnovas JM, Fernández-Soto D, et al. SARS-CoV-2 cysteine-like protease antibodies can be detected in serum and saliva of COVID-19–seropositive individuals. J Immunol 2020; 205: 3130-3140.
Tsilingiri K, de la Fuente H, Relaño M, Sánchez-Díaz R, Rodríguez C, Crespo J et al. oxLDL receptor in lymphocytes prevents atherosclerosis and predicts subclinical disease. Circulation 2019; 139: 243-255.
Baggen J, Hurdiss DL, Zocher G, Mistry N, Roberts RW, Slager JJ, H Guo H, van Vliet ALW, Wahedi M, Benschop K, Duizer E, de Haan CAM, de Vries E, Casasnovas JM, de Groot RJ, Arnberg N, Stehle T, Ranson NA, Thibaut H, van Kuppeveld FJM. A role of enhanced receptor engagement in the evolution of a pandemic acute haemorrhagic conjunctivitis virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2018; 115: 397-402.
Muñoz-Alía MA, Casasnovas JM, Celma ML, Carabaña J, Liton PB, Fernández-Muñoz R. Measles Virus Hemagglutinin epitopes immunogenic in natural infection and vaccination are targeted by broad or genotype-specific neutralizing monoclonal antibodies. Virus Res 2017; 236: 30-43.
Santiago C, Mudgal G, Reguera J, Recacha R, Albrecht S, Enjuanes L, Casasnovas JM. Allosteric inhibition of aminopeptidase N functions related to tumor growth and virus infection. Scientific Reports 2017; 7, 46045, doi: 10.1038/srep46045.
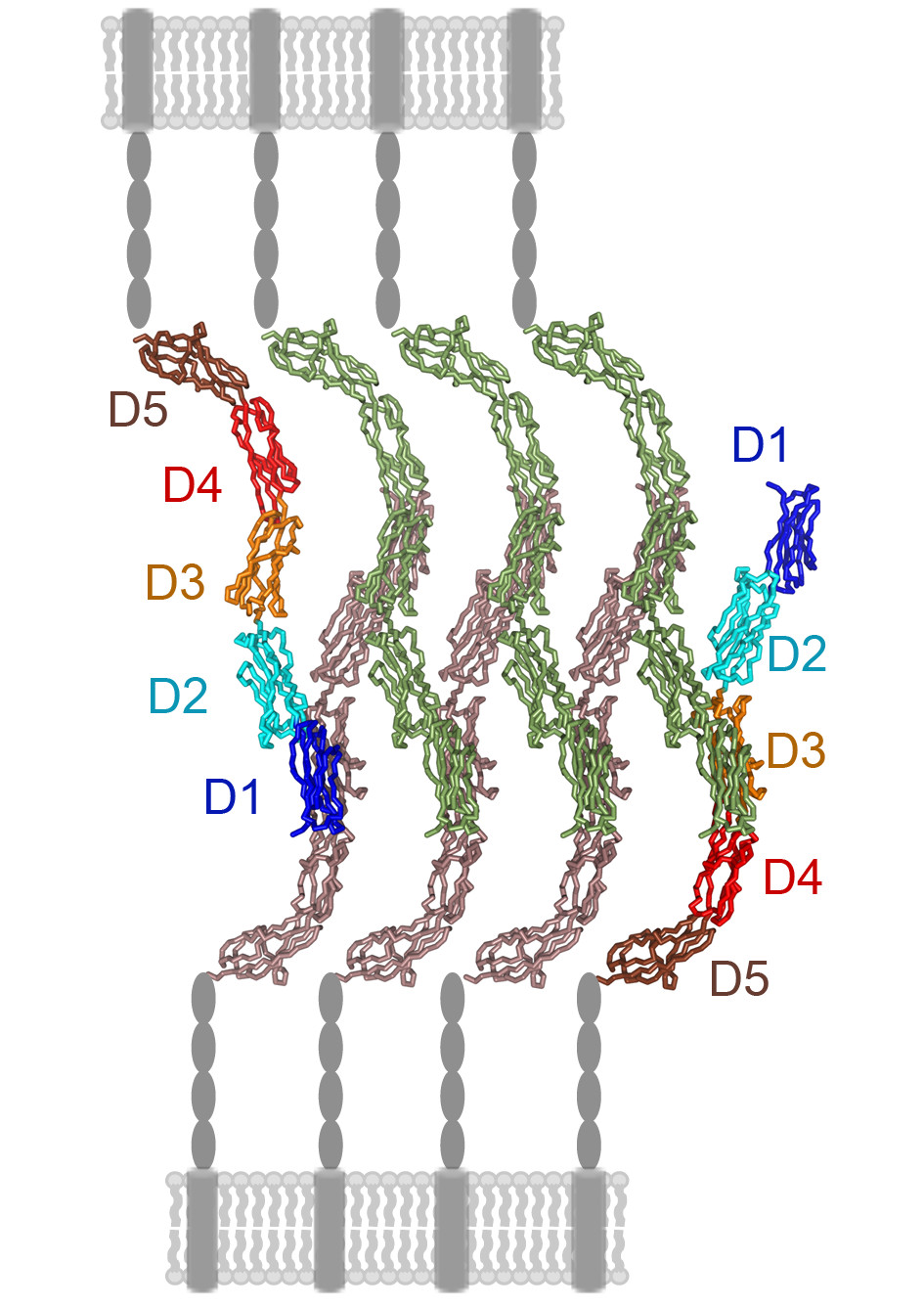 Our group studies the cell surface molecules that regulate the immune system and virus entry into host cells. We analyse receptor-ligand interactions related to immune processes such as cell adhesion and phagocytosis, as well as virus binding to cells. In addition, we characterise virus neutralization by humoral immune responses and its correlation with virus entry into cells. Our research has provided key observations regarding immune receptor function, and has identified viral epitopes essential for virus infection, some of which are targeted by neutralizing antibodies. Our multidisciplinary research applies structural (X-ray crystallography), biochemical and cell biology approaches.
Our group studies the cell surface molecules that regulate the immune system and virus entry into host cells. We analyse receptor-ligand interactions related to immune processes such as cell adhesion and phagocytosis, as well as virus binding to cells. In addition, we characterise virus neutralization by humoral immune responses and its correlation with virus entry into cells. Our research has provided key observations regarding immune receptor function, and has identified viral epitopes essential for virus infection, some of which are targeted by neutralizing antibodies. Our multidisciplinary research applies structural (X-ray crystallography), biochemical and cell biology approaches.
We are characterising antibodies (Abs) that neutralise Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV), Ebolavirus (EBOV) or the SARS-CoV-2, responsible of the COVID-19 pandemic. Using electron microscopy, we found that a potent anti-HIV-1 Ab binds to the CD4-receptor binding site in the HIV env protein (Figure 1); this Ab likely neutralises HIV because it inhibits virus cell entry. Using several methodologies we are identifying anti-EBOV antibodies, which are potential therapeutics for the treatment of Ebola disease.
During this year, we have produced the SARS-CoV-2 envelope spike (S) antigen, which is being used in serological tests completed at the CNB-CSIC.
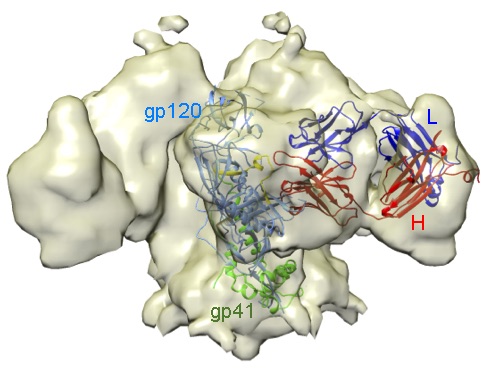
An antibody that neutralises HIV-1 and recognises the CD4 receptor binding site in the virus envelope glycoprotein. Electron density map of a trimeric HIV-1 gp140 protein in complex with a neutralising Ab. A monomer of the HIV-1 protein composed of the gp120 (blue) and the gp41 (green) subunits fitted in the map are shown as ribbons, together with the bound Ab (heavy chain in red y light chain in blue). The CD4 receptor-binding region in gp120 to which the Ab binds is in yellow.








