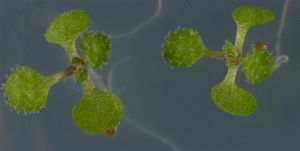
Plant Physiol. 2024 Apr 12:kiae213.
Fuster-Pons A, Murillo-Sánchez A, Méndez-Vigo B, Marcer A, Pieper B, Torres-Pérez R, Oliveros JC, Tsiantis M, Picó FX, Alonso-Blanco C.
Abstract
Natural variation in trichome pattern (amount and distribution) is prominent among populations of many angiosperms. However, the degree of parallelism in the genetic mechanisms underlying this diversity and its environmental drivers in different species remain unclear. To address these questions, we analyzed the genomic and environmental bases of leaf trichome pattern diversity in Cardamine hirsuta, a relative of Arabidopsis (Arabidopsis thaliana). We characterized 123 wild accessions for their genomic diversity, leaf trichome patterns at different temperatures, and environmental adjustments. Nucleotide diversities and biogeographical distribution models identified two major genetic lineages with distinct demographic and adaptive histories. Additionally, C. hirsuta showed substantial variation in trichome pattern and plasticity to temperature. Trichome amount in C. hirsuta correlated positively with spring precipitation but negatively with temperature, which is opposite to climatic patterns in A. thaliana. Contrastingly, genetic analysis of C. hirsuta glabrous accessions indicated that, like for A. thaliana, glabrousness is caused by null mutations in ChGLABRA1 (ChGL1). Phenotypic genome-wide association studies (GWAS) further identified a ChGL1 haplogroup associated with low trichome density and ChGL1 expression. Therefore, a ChGL1 series of null and partial loss-of-function alleles accounts for the parallel evolution of leaf trichome pattern in C. hirsuta and A. thaliana. Finally, GWAS also detected other candidate genes (e.g. ChETC3, ChCLE17) that might affect trichome pattern. Accordingly, the evolution of this trait in C. hirsuta and A. thaliana shows partially conserved genetic mechanisms but is likely involved in adaptation to different environments.- Las plantas adaptan su desarrollo y morfología según las condiciones ambientales de su entorno, como la duración del día y la temperatura
- La proteína COP1, además de regular el desarrollo de las plantas en la oscuridad, es responsable de su crecimiento en respuesta a temperaturas ambientes elevadas
- Un nuevo modelo basado en la regulación de COP1 permite predecir cómo el calentamiento global afecta el crecimiento de las plantas según la estación del año y latitud geográfica
Las plantas adaptan su desarrollo y morfología a las condiciones ambientales que las rodean, fundamentalmente, la duración del día y la temperatura ambiente. Estos dos factores afectan de manera directa al rendimiento de los cultivos, de ahí el interés de la comunidad científica en su estudio. Un trabajo de investigadores del Consejo Superior de Investigaciones Científicas (CSIC) presenta un modelo matemático basado en los procesos que modulan a los reguladores de la respuesta a temperatura en plantas, el cuál se ha entrenado con un notable número de datos experimentales.
Esta investigación, publicada en la revista Science Advances, es fruto de la colaboración entre los grupos dirigidos por Salomé Prat y Saúl Ares en el Centro Nacional de Biotecnología perteneciente al CSIC (CNB-CSIC) y Pablo Catalán del Grupo Interdisciplinar de Sistemas Complejos (GISC) de la Universidad Carlos III de Madrid.
Plant Cell Physiol. 2020 Mar 27. pii: pcaa041
Fernández-Santos R, Izquierdo Y, López A, Muñiz L, Martínez M, Cascón T, Hamberg M, Castresana C.
Abstract
Lipid Droplets (LDs) have classically been viewed as seed storage particles, yet they are now emerging as dynamic organelles associated with developmental and stress responses. Nevertheless, their involvement in plant immunity has still been little studied. Here, we found LD accumulation in Arabidopsis thaliana leaves that induced a hypersensitive defense response (HR) after Pseudomonas infection. We established a protocol to reproducibly isolate LDs and to analyze their protein content. The expression of GFP fusion proteins in Nicotiana benthamiana and in transgenic Arabidopsis lines validated the LD localization of glycerol-3-phosphate-acyltransferase 4 (GPAT4) and 8 (GPAT8), required for cutin biosynthesis. Similarly, we showed LD localization of α-dioxygenase1 (α-DOX1) and caleosin3 (CLO3), involved in the synthesis of fatty acid derivatives, and that of phytoalexin deficient 3 (PAD3), which is involved in camalexin synthesis. We found evidence suggesting the existence of different populations of LDs, with varying protein content and distributions. GPAT4 and GPAT8 were associated with LDs inside stomata and surrounding cells of untreated leaves, yet they were mainly confined to LDs in guard cells after bacterial inoculation. By contrast, α-DOX1 and PAD3 were associated with LDs in the epidermal cells of HR-responding leaves, with PAD3 mostly restricted to cells near dead tissue, while CLO3 had a more ubiquitous distribution. As such, the nature of the proteins identified, together with the phenotypic examination of selected mutants, suggest that LDs participate in lipid changes and in the production and transport of defense components affecting the interaction of plants with invading pathogens.
doi: 10.1093/pcp/pcaa041
- La regulación de la señalización mediada por ácido jasmónico es clave para mantener el equilibrio entre crecimiento y defensa
- Las proteínas BPM regulan la degradación de los factores de transcripción que activan la respuesta inmune.
La supervivencia de las plantas en la naturaleza requiere su adaptación a diferentes tipos de estrés medioambiental. A diferencia de los animales, las plantas no tienen posibilidad de escapar cuando se enfrentan a una agresión externa como la mordedura de un insecto. Por este motivo, han desarrollado mecanismos de señalización interna y respuesta a través de hormonas como el ácido jasmónico. Sin embargo, la respuesta desencadenada por esta hormona frena el crecimiento de la planta para centrar los recursos en la defensa. Así, un exceso de acción de esta hormona puede afectar al desarrollo vegetal, por lo que su señalización debe estar regulada de una manera muy precisa en tiempo e intensidad.
Ahora, investigadores del Centro Nacional de Biotecnología (CNB) pertenecientes al Consejo Superior de Investigaciones Científicas (CSIC) en colaboración con las universidades de Estrasburgo y Navarra han identificado un nuevo mecanismo molecular que modula los pulsos de activación de la hormona. El trabajo, que ha sido publicado en la revista Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS), da respuesta a cómo se regula la activación de defensas hasta alcanzar un equilibrio entre crecimiento y respuesta a estrés.
PLoS Genet. 2018 Mar 23;14(3):e1007296.
Yang Y, Nicolas M, Zhang J, Yu H, Guo D, Yuan R, Zhang T, Yang J, Cubas P, Qin G.
TIE1 promotes branching in Arabidopsis, leading to bushier plants. TIE1 carries out this function by interacting with BRANCHED1, another protein widely studied for its role in modulating plant architecture. Defining the processes that modulate branching in crop species might help to optimise agricultural production.
Sánchez-Bermejo E, Castrillo G, Navarro C, del Llano B, Zarco-Fernández S, Martinez-Herrera DJ, Leo-del Puerto Y, Muñoz R, Cámara C, Paz-Ares J, Alonso-Blanco C, Leyva A.
 The enormous amount of environmental arsenic was a major factor in determining the biochemistry of incipient life forms early in the Earth’s history. The most abundant chemical
form in the reducing atmosphere was arsenite, which forced organisms to evolve strategies to manage this chemical species. Following the great oxygenation event, arsenite oxidized to arsenate and the action of arsenate reductases became a central survival requirement. The identity of a biologically relevant arsenate reductase in plants nonetheless continues to be debated.
The enormous amount of environmental arsenic was a major factor in determining the biochemistry of incipient life forms early in the Earth’s history. The most abundant chemical
form in the reducing atmosphere was arsenite, which forced organisms to evolve strategies to manage this chemical species. Following the great oxygenation event, arsenite oxidized to arsenate and the action of arsenate reductases became a central survival requirement. The identity of a biologically relevant arsenate reductase in plants nonetheless continues to be debated.
Here we identify a quantitative trait locus that encodes a novel arsenate reductase critical for arsenic tolerance in plants. Functional analyses indicate that several non-additive polymorphisms affect protein structure and account for the natural variation in arsenate reductase activity in Arabidopsis thaliana accessions. This study shows that arsenate reductases are an essential component for natural plant variation in As(V) tolerance.
Manzano-Piedras E, Marcer A, Alonso-Blanco C, Picó FX.
The role that different life-history traits may have in the process of adaptation caused by divergent selection can be assessed by using extensive collections of geographically-explicit populations. This is because adaptive phenotypic variation shifts gradually across space as a result of the geographic patterns of variation in environmental selective pressures. Hence, large-scale experiments are needed to identify relevant adaptive life-history traits as well as their relationships with putative selective agents.
We conducted a field experiment with 279 geo-referenced accessions of the annual plant Arabidopsis thaliana collected across a native region of its distribution range, the Iberian Peninsula. We quantified variation in life-history traits throughout the entire life cycle. We built a geographic information system to generate an environmental data set encompassing climate, vegetation and soil data. We analysed the spatial autocorrelation patterns of environmental variables and life-history traits, as well as the relationship between environmental and phenotypic data. Almost all environmental variables were significantly spatially autocorrelated. By contrast, only two life-history traits, seed weight and flowering time, exhibited significant spatial autocorrelation. Flowering time, and to a lower extent seed weight, were the life-history traits with the highest significant correlation coefficients with environmental factors, in particular with annual mean temperature. In general, individual fitness was higher for accessions with more vigorous seed germination, higher recruitment and later flowering times. Variation in flowering time mediated by temperature appears to be the main life-history trait by which A. thaliana adjusts its life history to the varying Iberian environmental conditions.
The use of extensive geographically-explicit data sets obtained from field experiments represents a powerful approach to unravel adaptive patterns of variation. In a context of current global warming, geographically-explicit approaches, evaluating the match between organisms and the environments where they live, may contribute to better assess and predict the consequences of global warming.
BMC Plant Biol. 2014; 14(1): 17.
Brennan AC, Méndez-Vigo B, Haddioui A, Martínez-Zapater JM, Picó FX, Alonso-Blanco C.
 Deciphering the genetic structure of Arabidopsis thaliana diversity across its geographic range provides the bases for elucidating the demographic history of this model plant. Despite the unique A. thaliana genomic resources currently available, its history in North Africa, the extreme southern limit in the biodiversity hotspot of the Mediterranean Basin, remains virtually unknown.
Deciphering the genetic structure of Arabidopsis thaliana diversity across its geographic range provides the bases for elucidating the demographic history of this model plant. Despite the unique A. thaliana genomic resources currently available, its history in North Africa, the extreme southern limit in the biodiversity hotspot of the Mediterranean Basin, remains virtually unknown.
To approach A. thaliana evolutionary history in North Africa, we have analysed the genetic diversity and structure of 151 individuals collected from 20 populations distributed across Morocco. Genotyping of 249 genome-wide SNPs indicated that Morocco contains substantially lower diversity than most analyzed world regions. However, IBD, STRUCTURE and PCA clustering analyses showed that genetic variation is strongly geographically structured. We also determined the genetic relationships between Morocco and the closest European region, the Iberian Peninsula, by analyses of 201 populations from both regions genotyped with the same SNPs. These analyses detected four genetic groups, but all Moroccan accessions belonged to a common Iberian/Moroccan cluster that appeared highly differentiated from the remaining groups. Thus, we identified a genetic lineage with an isolated demographic history in the south-western Mediterranean region. The existence of this lineage was further supported by the study of several flowering genes and traits, which also found Moroccan accessions similar to the same Iberian group. Nevertheless, genetic diversity for neutral SNPs and flowering genes was higher in Moroccan than in Iberian populations of this lineage. Furthermore, we analyzed the genetic relationships between Morocco and other world regions by joint analyses of a worldwide collection of 337 accessions, which detected an additional weak relationship between North Africa and Asia.
The patterns of genetic diversity and structure of A. thaliana in Morocco show that North Africa is part of the species native range and support the occurrence of a glacial refugium in the Atlas Mountains. In addition, the identification of a genetic lineage specific of Morocco and the Iberian Peninsula indicates that the Strait of Gibraltar has been an A. thaliana migration route between Europe and Africa. Finally, the genetic relationship between Morocco and Asia suggests another migration route connecting north-western Africa and Asia
Journal of Experimental Botany
Méndez-Vigo B, Andrés MT, Ramiro M, Martínez-Zapater JM & Alonso-Blanco C.
Vegetative growth and flowering initiation are two crucial developmental processes in the life cycle of annual plants that are closely associated. The timing of both processes affects several presumed adaptive traits, such as flowering time (FT), total leaf number (TLN), or the rate of leaf production (RLP). However, the interactions among these complex processes and traits, and their mechanistic bases, remain largely unknown. To determine the genetic relationships between them, the natural genetic variation between A. thaliana accessions Fei-0 and Ler has been studied using a new population of 222 LerxFei-0 recombinant inbred lines. Temporal analysis of the parental development under a short day photoperiod distinguishes two vegetative phases differing in their RLP. QTL mapping of RLP in consecutive time intervals of vegetative development indicates that Ler/Fei-0 variation is caused by 10 loci whose small to moderate effects mainly display two different temporal patterns. Further comparative QTL analyses show that most of the genomic regions affecting FT or TLN also alter RLP. In addition, the partially independent genetic bases observed for FT and TLN appear determined by several genomic regions with two different patterns of phenotypic effects: regions with a larger effect on FT than TLN, and vice versa. The distinct temporal and pleiotropic patterns of QTL effects suggest that natural variation for flowering time is caused by different genetic mechanisms involved in vegetative and/or reproductive phase changes, most of them interacting with the control of leaf production rate. Thus, natural selection might contribute to maintain this genetic variation due to its phenotypic effects not only on the timing of flowering initiation but also on the rate of vegetative growth.COOKIES POLICY
A cookie is a text file that is stored on your computer or mobile device via a web server and only that server will be able to retrieve or read the contents of the cookie and allow the Web site remember browser preferences and navigate efficiently. Cookies make the interaction between the user and the website faster and easier.
General information
This Website uses cookies. Cookies are small text files generated by the web pages you visit, which contain the session data that can be useful later in the website. In this way this Web remembers information about your visit, which can facilitate your next visit and make the website more useful.
How do cookies?
Cookies can only store text, usually always anonymous and encrypted. No personal information is ever stored in a cookie, or can be associated with identified or identifiable person.
The data allow this website to keep your information between the pages, and also to discuss how to interact with the website. Cookies are safe because they can only store information that is put there by the browser, which is information the user entered in the browser or included in the page request. You can not run the code and can not be used to access your computer. If a website encrypts cookie data, only the website can read the information.
What types of cookies used?
The cookies used by this website can be distinguished by the following criteria:
1. Types of cookies as the entity that manages:
Depending on who the entity operating the computer or domain where cookies are sent and treat the data obtained, we can distinguish:
- Own cookies: are those that are sent to the user's terminal equipment from a computer or domain managed by the editor itself and from which provides the service requested by the user.
- Third party cookies: these are those that are sent to the user's terminal equipment from a machine or domain that is not managed by the publisher, but by another entity data is obtained through cookies.
In the event that the cookies are installed from a computer or domain managed by the editor itself but the information collected by these is managed by a third party can not be considered as party cookies.
2. Types of cookies as the length of time that remain active:
Depending on the length of time that remain active in the terminal equipment can be distinguished:
- Session cookies: cookies are a type designed to collect and store data while the user accesses a web page. Are usually used to store information that only worth preserving for the service requested by the user at any one time (eg a list of products purchased).
- Persistent cookies: cookies are a type of data which are stored in the terminal and can be accessed and treated for a period defined by the head of the cookie, and can range from a few minutes to several years.
3. Cookies types according to their purpose:
Depending on the purpose for which the data are processed through cookies, we can distinguish between:
- Technical cookies: these are those that allow the user to navigate through a web page or application platform and the use of different options or services it exist as, for example, control traffic and data communication, identify the session, access to restricted access parts, remember the elements of an order, make the buying process an order, make an application for registration or participation in an event, use security features while browsing store content for dissemination videos or sound or share content via social networks.
- Customization cookies: these are those that allow the user to access the service with some general characteristics based on a predefined set of criteria in the user terminal would eg language, the type of browser through which you access the service, the locale from which you access the service, etc.
- Analysis cookies: they are those that allow the responsible for them, monitoring and analyzing the behavior of users of the web sites that are linked. The information gathered through such cookies are used in measuring the activity of web sites, application or platform and for the profiling of user navigation of such sites, applications and platforms, in order to make improvements function data analysis how users use the service.
Management tool cookies
This Website uses Google Analytics.
Google Analytics is a free tool from Google that primarily allows website owners know how users interact with your website. Also, enable cookies in the domain of the site in which you are and uses a set of cookies called "__utma" and "__utmz" to collect information anonymously and reporting of website trends without identifying individual users..
For statistics of use of this website use cookies in order to know the level of recurrence of our visitors and more interesting content. This way we can concentrate our efforts on improving the most visited areas and make the user more easily find what they are looking for. On this site you can use the information from your visit for statistical evaluations and calculations anonymous data and to ensure the continuity of service or to make improvements to their websites. For more details, see the link below privacy policy [http://www.google.com/intl/en/policies/privacy/]
How to manage cookies on your computer: disabling and deleting cookies
All Internet browsers allow you to limit the behavior of a cookie or disable cookies within settings or browser settings. The steps for doing so are different for each browser, you can find instructions in the help menu of your browser.
If you decline the use of cookies, since it is possible thanks to the preferences menu of your browser or settings, reject, this website will continue to function properly without the use of the same.
Can you allow, block or delete cookies installed on your computer by setting your browser options installed on your computer:
- For more information about Internet Explorer click here.
- For more information on Chrome click here.
- For more information about Safari click here.
- For more information about Firefox click here.
Through your browser, you can also view the cookies that are on your computer, and delete them as you see fit. Cookies are text files, you can open and read the contents. The data within them is almost always encrypted with a numeric key corresponding to an Internet session so often has no meaning beyond the website who wrote it.
Informed consent
The use of this website on the other hand, implies that you paid your specific consent to the use of cookies, on the terms and conditions provided in this Cookies Policy, without prejudice to the measures of deactivation and removal of cookies that you can take, and mentioned in the previous section.