Signalling by Kinases in Inflammation and Cancer
RESEARCH GROUPS

Ana Cuenda
Group Leader
Research Summary
The aim of our group is to understand the role of stress activated protein kinases, particularly p38MAPKs, in physiology and disease. These kinases regulate diverse cellular functions in normal conditions and in response to environmental stress, infection and proinflammatory cytokines. Moreover, they become deregulated in several human disease situations such as oncogenic transformation and inflammation, making them promising targets for new therapeutic avenues.
Research Lines
We are interested in how stress kinases enable cells to sense and adapt to internal and external cues by modulating cellular responses and behavior -particularly in the context of inflammation and cancer. Our research focuses on the stress-activated p38 MAPK pathways, especially the lesser-studied isoforms p38γand p38δ. We investigate their roles in:
- Chronic inflammation leading to cancer development (e.g., colitis-associated colon cancer and metastasis)
- Host responses to pathogen infections
- The resolution of inflammation during tissue repair
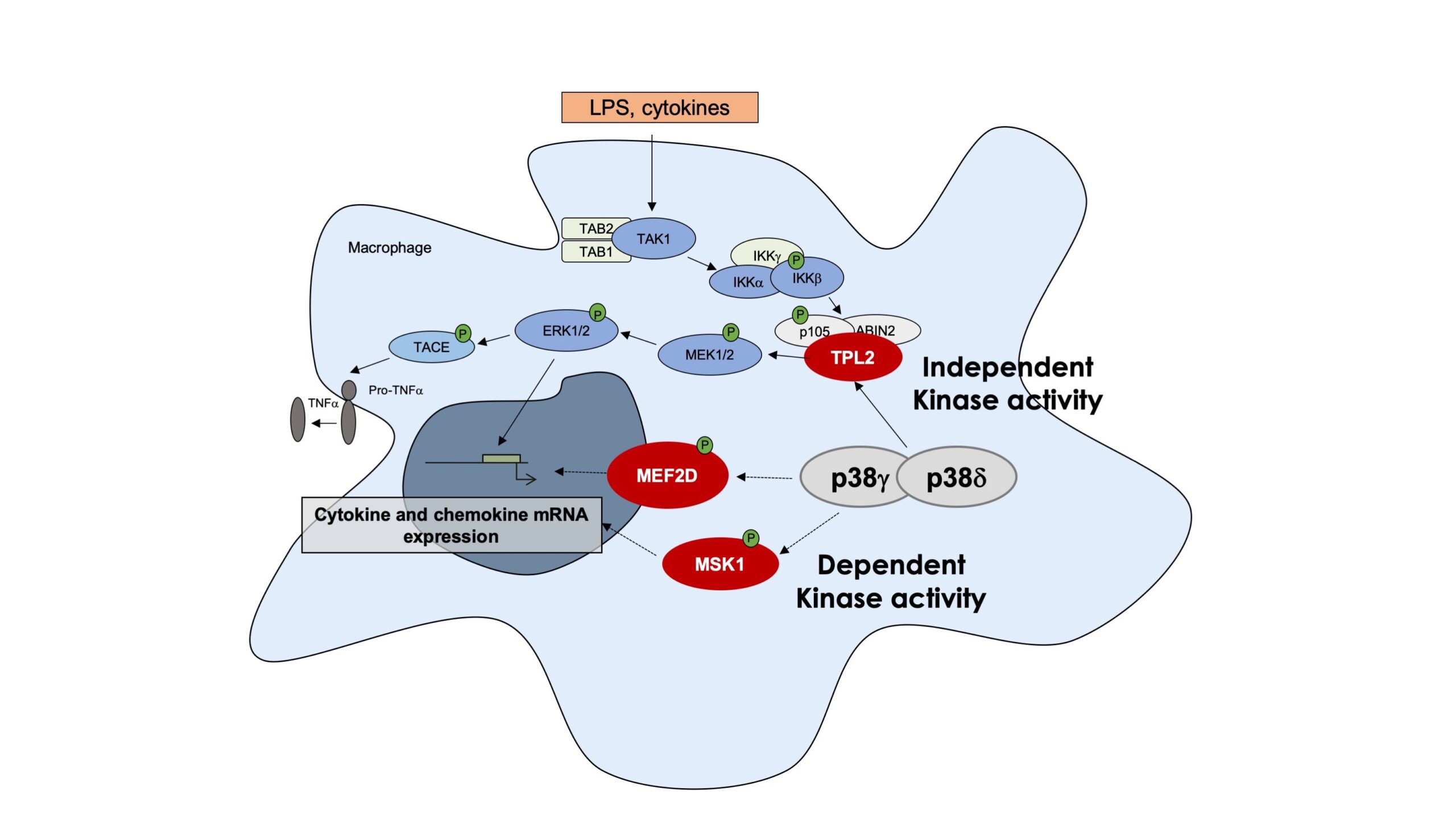
Schematic of the kinase dependent and independent functions of p38γ and p38δ in activated macrophages.
Our work has uncovered the molecular mechanisms through which p38γ and p38δ regulate inflammatory gene expression and integrate signaling pathways under both homeostatic and stress conditions. We have provided in vivo evidence of their involvement in immune responses to infections, such as Candida albicans, and in the progression of inflammatory diseases, including colitis and rheumatoid arthritis, as well as their contribution to skin and colon cancer development.
To explore these questions, we combine biochemical approaches and chemical biology with cellular studies and in vivo models, including transgenic and isoform-specific p38-deficient mice. Our current research projects focus on:
- Inflammation-driven tumorigenesis
- Crosstalk between cancer cells and stromal cells in the tumor microenvironment, including during metastasis
- Regulation of gut microbiota and microbe-host interactions within the tumor setting
Additionally, we are actively pursuing the discovery of novel p38 MAPK substrates, binding partners, and small-molecule inhibitors, and studying their physiological roles using advanced cellular systems and genetically engineered mouse models.”
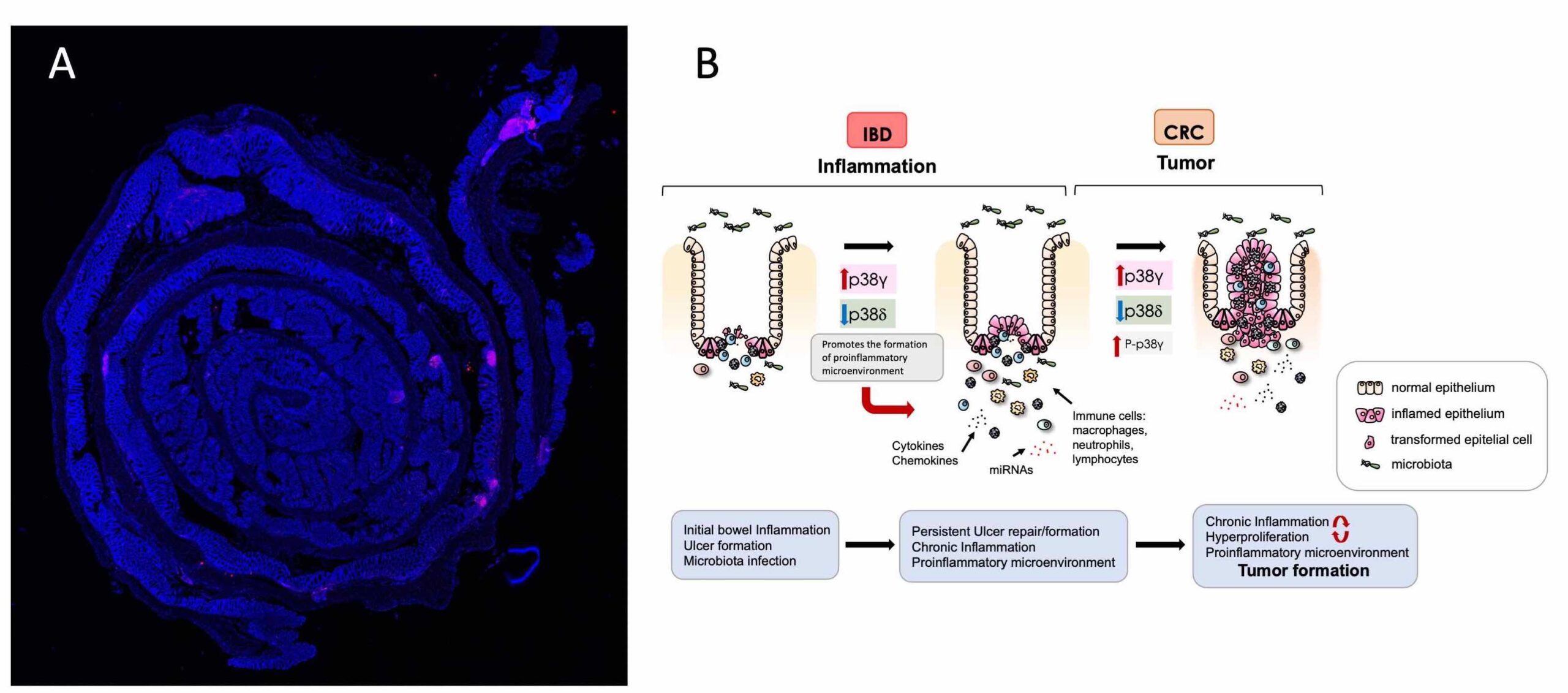
(A) Representative immunofluorescence image of colon sections from mice treated with AOM/DSS. DAPI (blue) and CD3+ cells (red) are shown.
(B) Schematic illustration of the function of alternative p38MAPKs, p38γ and p38δ, in IBD and CRC formation.
Publications
Group Members
Group Leader
Ana Cuenda
Lab assistant
Ruth Gómez-Caro
Staff scientist
Ana Mª Risco Cruz
Postdoctoral Researchers
Ester Díaz Mora
Pilar Fajardo Flores
PhD candidates
Daniel Mora Diego
Marta Meireles da Silva Gil
Alberto Bigogno
Vicente Labella Guerrero








